Google clarifies JavaScript rendering implications of 'noindex' tags
Google clarifies JavaScript rendering implications of 'noindex' tags
Google has updated its JavaScript SEO documentation to provide more clarity on how its crawler handles noindex tags on pages that rely on JavaScript. This update highlights potential issues with removing or altering noindex directives through JavaScript and provides important guidance for webmasters managing JavaScript-heavy sites.
The Key Update
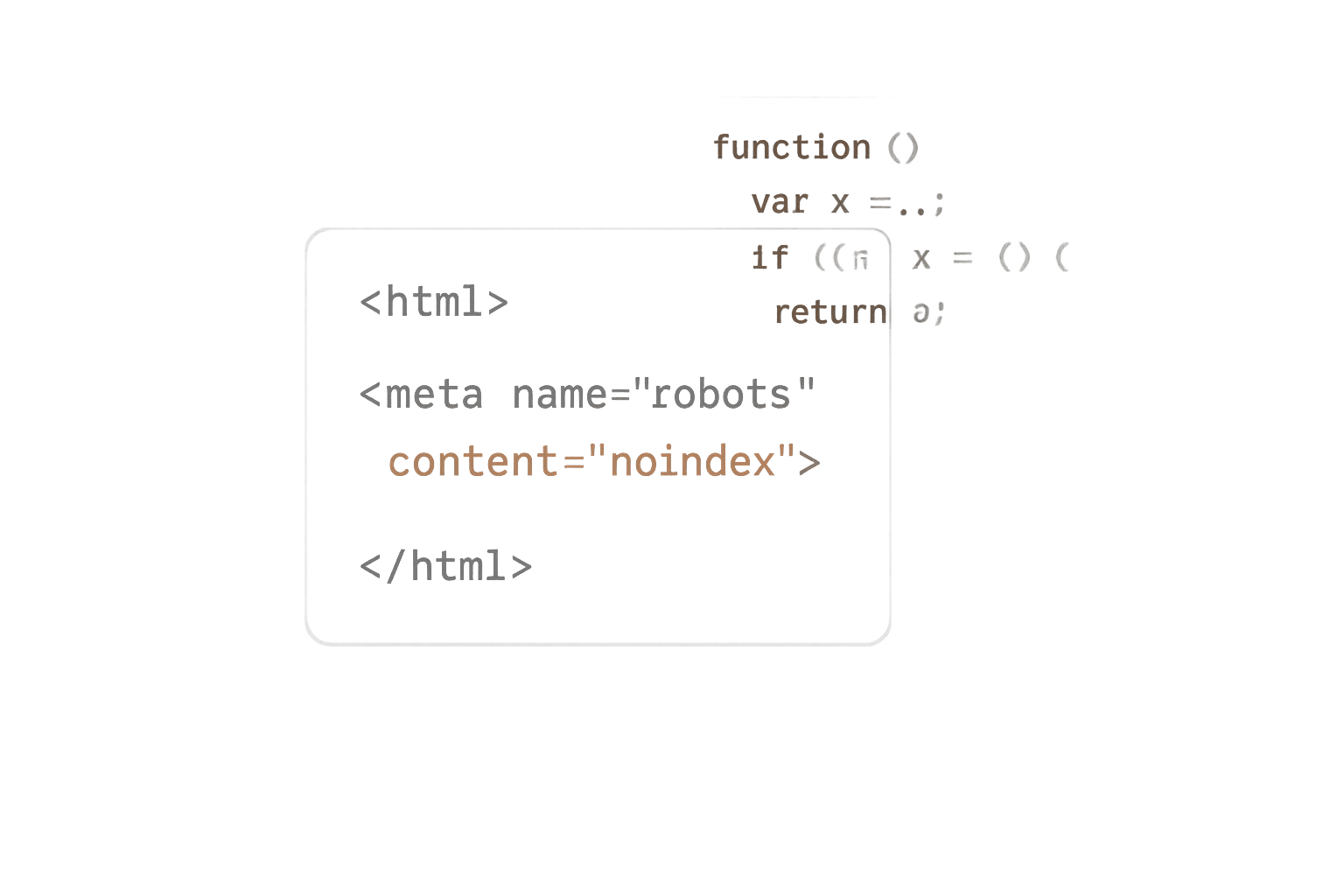
The clarification addresses a scenario where a page includes a noindex tag in its initial response, and JavaScript is later used to modify or remove it. According to Google, this approach may not work as intended.
The updated guidance, which appears under the section on robots meta tags for JavaScript pages, states:
"When Google encounters the
noindextag, it may skip rendering and JavaScript execution, which means using JavaScript to change or remove the robotsmetatag fromnoindexmay not work as expected. If you do want the page indexed, don’t use anoindextag in the original page code."
This makes it clear that Google's crawler may bypass the rendering step entirely if it detects a noindex tag in the initial HTML, preventing any subsequent JavaScript from executing.
sbb-itb-0f47b19
Context for the Change
Google explained the update further on its documentation updates page, noting that while its system can render JavaScript pages, the behavior in this specific situation "is not well defined and might change."
This clarification addresses a common implementation method on JavaScript-heavy websites, where noindex tags are initially applied and then removed dynamically after content successfully loads. Google’s updated guidance warns that such reliance on JavaScript to modify noindex may lead to indexing issues.
Why It Matters
For webmasters and SEO professionals managing JavaScript sites, this update underscores the need for proper handling of noindex directives. Some websites use noindex as a placeholder when content fails to load or during API call failures, and then remove it with JavaScript once the content becomes available.
Google emphasizes that this practice could cause problems:
"If you do want the page indexed, keep
noindexout of the original response and use server-side handling for error states (for example, appropriate status codes) when you truly want a page excluded."
By skipping the rendering process when a noindex tag is encountered, Google’s crawler may prevent these pages from being indexed, even if they appear indexable in a fully rendered browser.
Recommendations for Webmasters
To avoid indexing issues, Google advises against including a noindex tag in the initial HTML if there is any possibility that the page should be indexed. Instead, consider using server-side handling to manage error states or exclusion scenarios appropriately.
For those auditing JavaScript-heavy websites, it’s important to review pages with noindex in their initial code and ensure they do not rely on JavaScript to remove or modify the directive later. Such reliance could render the pages ineligible for indexing, even if they seem to function correctly when viewed in a browser.
Final Thoughts
This clarification in Google’s JavaScript SEO documentation addresses a significant implementation gap for webmasters. By making it clear that JavaScript cannot reliably alter noindex directives once they are present in the initial response, Google is helping site owners avoid potential indexing pitfalls and improve their SEO strategies. As always, adhering to Google’s best practices will help ensure better results in search indexing and performance.